Polyethylene Glycol, commonly abbreviated as PEG, is one of those materials that quietly powers multiple industries without most people ever noticing it. From medicines and skincare products to industrial manufacturing and chemical processing, PEG plays a vital role thanks to its unique chemical structure and performance characteristics.
Understanding the applications of polyethylene glycol helps explain why it has become a widely adopted compound across the medical, cosmetic, and industrial sectors.
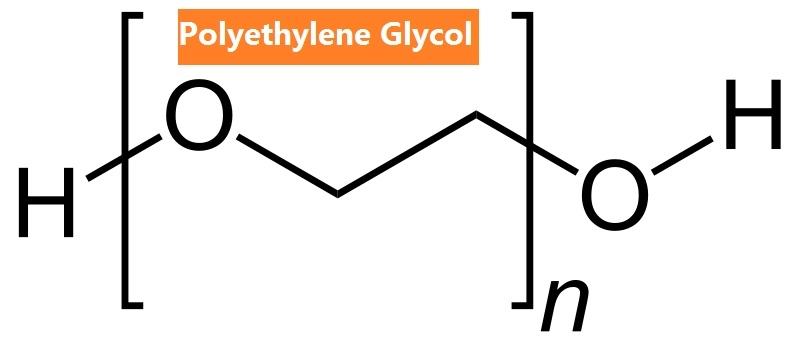
Polyethylene Glycol is a synthetic polymer formed by the polymerization of ethylene oxide. It is typically available in a wide range of molecular weights, which directly influence its physical form—from clear liquids to waxy solids or flakes. This flexibility is one of the main reasons PEG is used in so many different applications.
PEG is often identified by a number (such as PEG 400 or PEG 6000), which indicates its average molecular weight. Lower-molecular-weight PEGs tend to be liquids, while higher-molecular-weight versions appear as solids. Importantly, polyethylene glycol is odorless, colorless, non-volatile, and generally regarded as chemically stable, making it suitable for both consumer and industrial use.
The widespread use of polyethylene glycol is not accidental. Its popularity is driven by a combination of properties that are difficult to replicate with other compounds.
One of PEG’s most valuable characteristics is its excellent water solubility. PEG dissolves easily in water and many organic solvents, allowing it to function as a solvent, carrier, or dispersion medium. This makes it especially useful in pharmaceutical formulations and cosmetic products.
Another important property is its chemical inertness. PEG does not readily react with other ingredients, which improves formulation stability and shelf life. In addition, PEG exhibits low toxicity and good biocompatibility, particularly in controlled medical and personal care applications.
Finally, the ability to precisely control PEG’s molecular weight allows manufacturers to tailor its viscosity, melting point, and functional behavior. This tunability is what enables PEG to perform effectively as a lubricant, humectant, plasticizer, or binding agent depending on the application.

One of the most well-known uses of polyethylene glycol is in the medical and pharmaceutical industry. PEG is widely used in laxatives, where it functions as an osmotic agent that helps retain water in the bowel, easing constipation gently and effectively.
Beyond digestive health, PEG plays a crucial role in drug delivery systems. It is commonly used as an excipient in tablets, capsules, and injectable formulations to improve drug solubility and stability. In advanced pharmaceutical applications, a process known as PEGylation involves attaching PEG chains to drug molecules. This technique can extend a drug’s circulation time in the body, reduce immune responses, and improve overall therapeutic performance.
PEG is also used in medical creams, ointments, and gels, where its moisture-retaining and stabilizing properties enhance texture and effectiveness. Due to its established safety profile, polyethylene glycol remains a trusted ingredient in many regulated healthcare products.

In the cosmetics and personal care industry, polyethylene glycol is valued for both its performance and formulation flexibility. PEG functions as an emulsifier, helping oil- and water-based ingredients blend smoothly in creams, lotions, and cleansers. Without PEG, many skincare products would separate or feel uneven on the skin.
PEG also acts as a humectant, meaning it helps attract and retain moisture. This property is especially beneficial in products such as facial moisturizers, shampoos, conditioners, and body washes, where hydration and smooth texture are essential.
Additionally, polyethylene glycol improves the spreadability and sensory feel of cosmetic formulations. It helps products glide easily over the skin or hair, enhancing user experience. For manufacturers, PEG contributes to formulation stability, consistent quality, and longer shelf life—all critical factors in competitive beauty markets.
Outside of healthcare and cosmetics, polyethylene glycol is widely used in industrial and technical applications. In manufacturing environments, PEG serves as a lubricant and plasticizer, reducing friction and improving flexibility in materials such as plastics, rubber, and ceramics.
PEG is also commonly used as a processing aid in chemical production, textiles, and resins. Its ability to control viscosity and dispersion makes it valuable in coatings, inks, and adhesives. In some industrial cleaning formulations, polyethylene glycol enhances solubility and cleaning efficiency without excessive harshness.
Furthermore, PEG is used in laboratory settings, as a heat transfer fluid, and in certain food-contact or packaging applications, depending on regulatory approval and grade selection. This versatility reinforces polyethylene glycol’s position as a multifunctional material across diverse industries.